Kubernetes For Product Managers and Scrum Masters.
Here we are not going through any in-depth technology. What we are covering is the high-level overview of Kubernetes from a non-technical perspective.
Yes, we do not need to be a master of these technologies. But when we start searching to know about this technology overview, we will end up in the technical documentation. It is either a developer guide or an administration guide. It is not going to help us to get a high-level overview of the technology.

This module is purely for Product managers, project managers, scrum masters or support managers who wish to have a high-level overview of Kubernetes. If you are not interested in the non-technical aspects of Kubernetes, kindly skip this module and start with Kubernetes in 7 days? In a week
Why are a lot of discussions now on Kubernetes in the Techworld?
As you already know, the tech world is undergoing a drastic change. If we are not getting into that ship, we may end up in the seashore itself.

Hurry up, let’s get into the ship.
Kubernetes is an open-source project initiated by Google. They run their infrastructure on Kubernetes. Google is well-known for high performing infrastructure. When they made it open-source, everyone in Techworld started looking into it. Now Kubernetes is managed by CNCF. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation is a non-profit organization hosting critical infrastructure projects like,
- Containerd
- CoreDNS
- etcd
- Fluentd
- Helm
- Kubernetes
- Prometheus
- CRI-O
What is Kubernetes?
In the shipyard, we have cargo ship, controllership, and container registory etc.
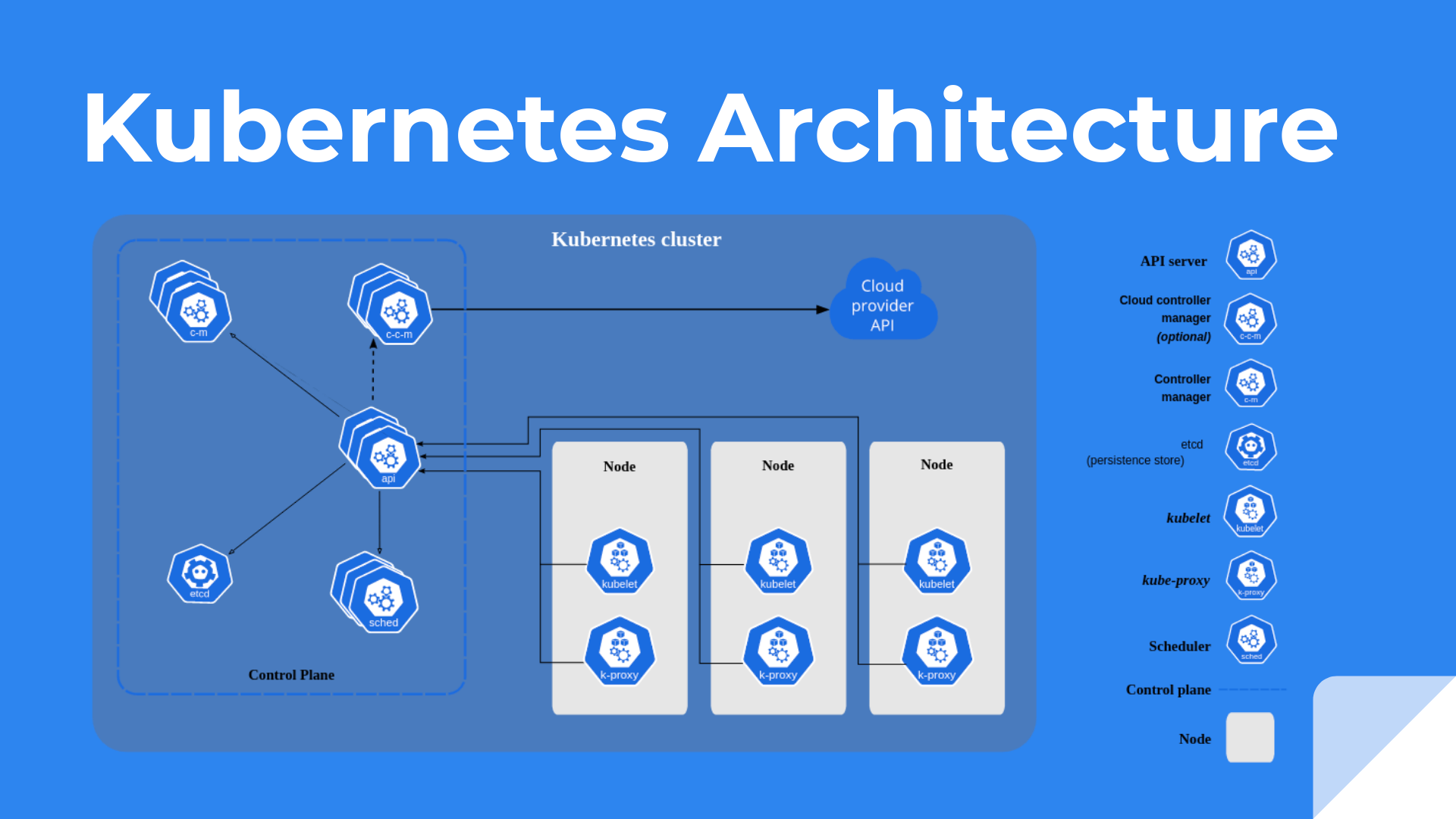
In the same way, we have identical components in the Kubernetes like scheduler, controller manager, worker node…
Kubernetes is a container ( microservice ) orchestrator. It automates container-based application deployment. It took over the market mainly because of the below features.
- Speed of deployment
- Faster auto-scaling
- Quicker upgrade and rollback
- Quicker recovery Let us dive in a little in-depth,
What is docker or a microservice?
Kubernetes is a container orchestrator. So what is a container?
Docker itself is another big topic. The idea of docker evolved from the shipping industries. It uses the same thought behind cargo containers. We will discuss this in another module. Now let us have a look at it from the viewpoint of Kubernetes.
The problem faced in the shipping industry.
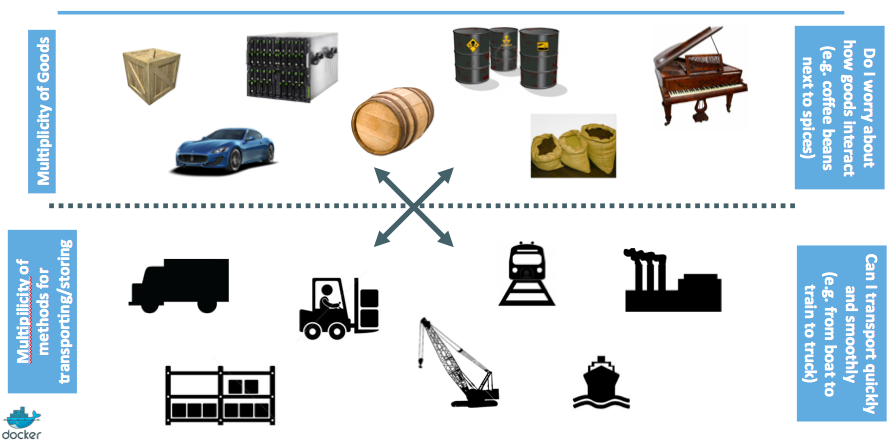
- Each goods item was treated separately.
- It consumes lots of time.
- The loss and damage of the goods items were higher.
The solution to the problem.
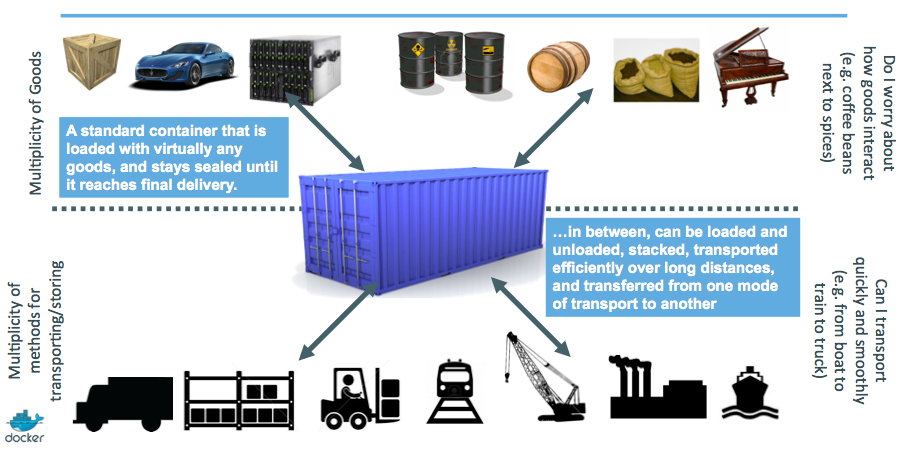
The solution to this problem was containerisation. Goods loaded in standard containers.
- The standardised container is loaded with all kinds of goods and sealed.
- Need not worry about how the containers are treated.
- Can transport quickly and smoothly.
- All kinds of transport mechanisms like the train, the truck crane can be used.
How does docker fit into this?
Docker container is lightweight OS instant packed with the application or portal or a database or whatever service you wanted to containerize.
Docker and container not the same?
Now we used the word docker container!! Are docker and container not the same?
No, it is not! To have a clear understanding, we need to go a little in-depth.
Don’t worry, let us go. It is not rocket science. Here we need to understand,
- Docker image
- Docker container
What is a docker image?
Docker images are read-only templates. If you are familiar with the Vmware template, you can relate it to the docker image. It is a mini OS template. Or the docker image is a file. It does not require any computing power ( CPU or memory ). Docker images are available/kept in,
- Docker hub.
- Google container registry.
- Almost all cloud providers have the option to create a docker registry.
- In your private registry.
- Or directly on your system.
Then what is docker containers?
Docker containers are runnable instances of a docker image. It requires CPU, memory and other computing resources to run. It is a mini VM. Since it called a microservice may be, we can call it a micro virtual machine :).
Docker container is lightweight OS instant packed with the application or portal or a database or whatever service you wanted to containerize.
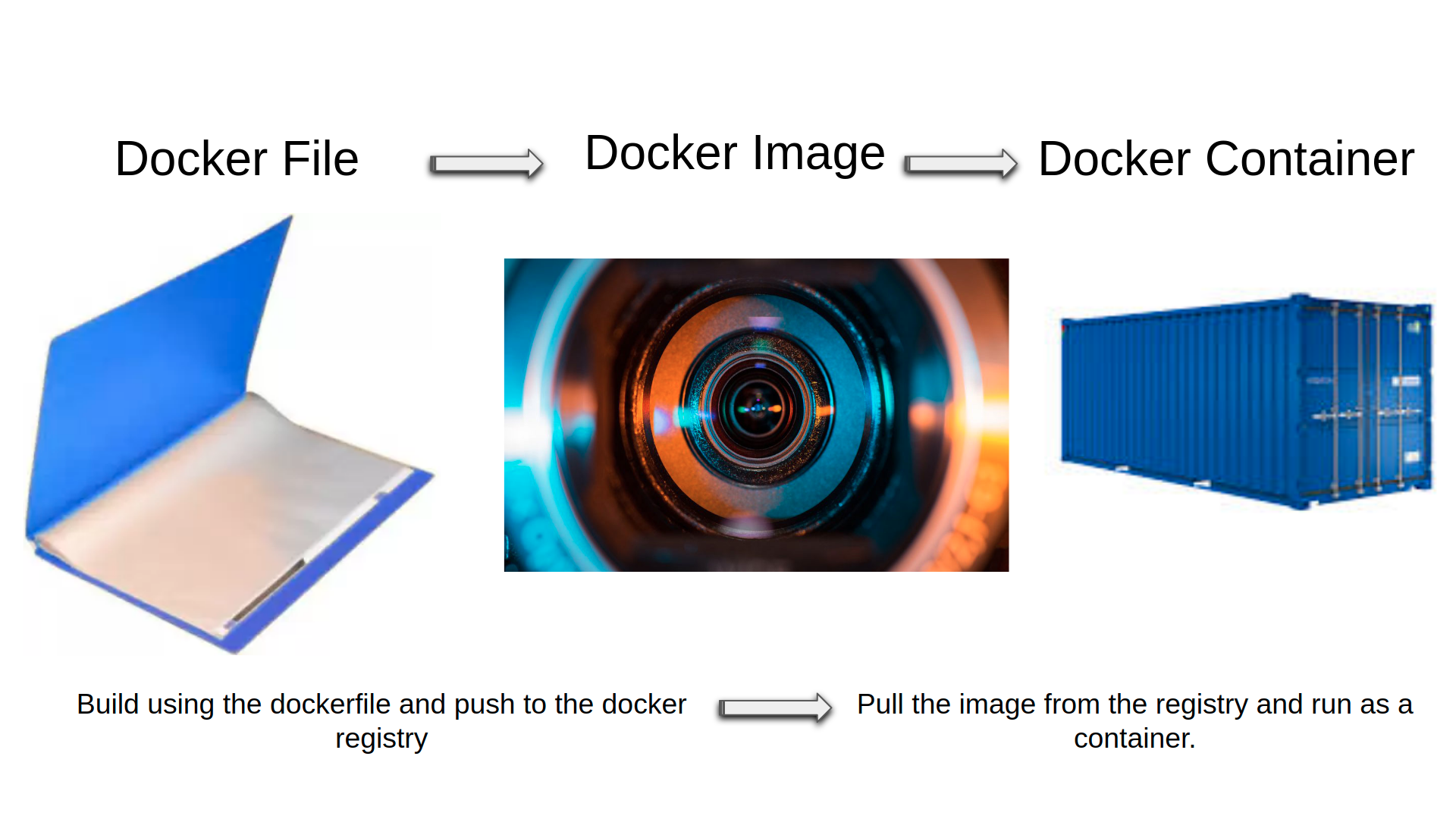
What is Dockerfile ?
Yes, we did not discuss the docker file. A Dockerfile is a text file that contains all the information needed to build a docker image.
- It has information like a base image.
- Information like any additional package needs on this image.
- Step by step command to assemble the image.
- Startup commands and arguments which is need during the container start.
Then what is the purpose of Kubernetes here?
We will go back to our office. Developers, testers, system administrators, service desk engineers are enough to run the business. But why we managers are needed there? They all are great, but someone should be available to manage and give a vision to them.
That is what the Kubernetes does here.
Is that the only solution available to manage the containers?

No, there are a few more container orchestrators/clusters available in the market.
- Kubernetes
- Mesos
- Docker swarm
These are the most commonly used solutions. But Kubernetes is widely adopted in the market. The word cluster is not the right fit here. For ease of understanding, I am using the word cluster. Yet right fit is the container orchestrator. I am tired of writing the word Kubernetes. I am going to use k8s from now.
Why are techies calling it K8S?
Kubernetes is also known as K8s. The abbreviation k8s came by shrinking the word Kubernetes. The letter “K” is followed by eight letters and ends with “S”.
- K - ubernete - s
- k - 8 - s
- k 8 s
- k8s
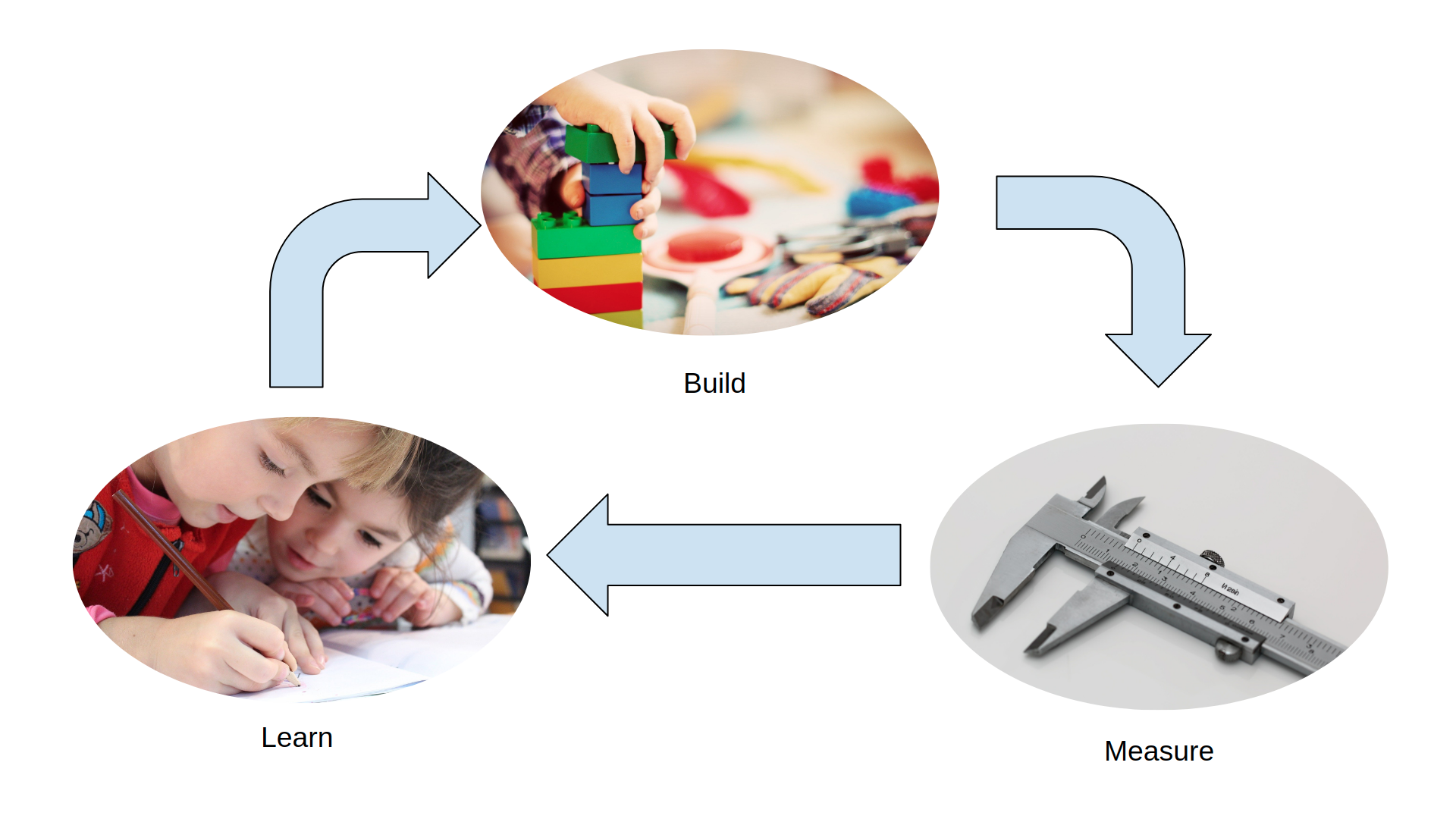
Why K8S? What makes it unique?
It minimizes the amount of time taken to build, measure, learn cycles.
The product development team does not need to worry about the underlying infrastructure.
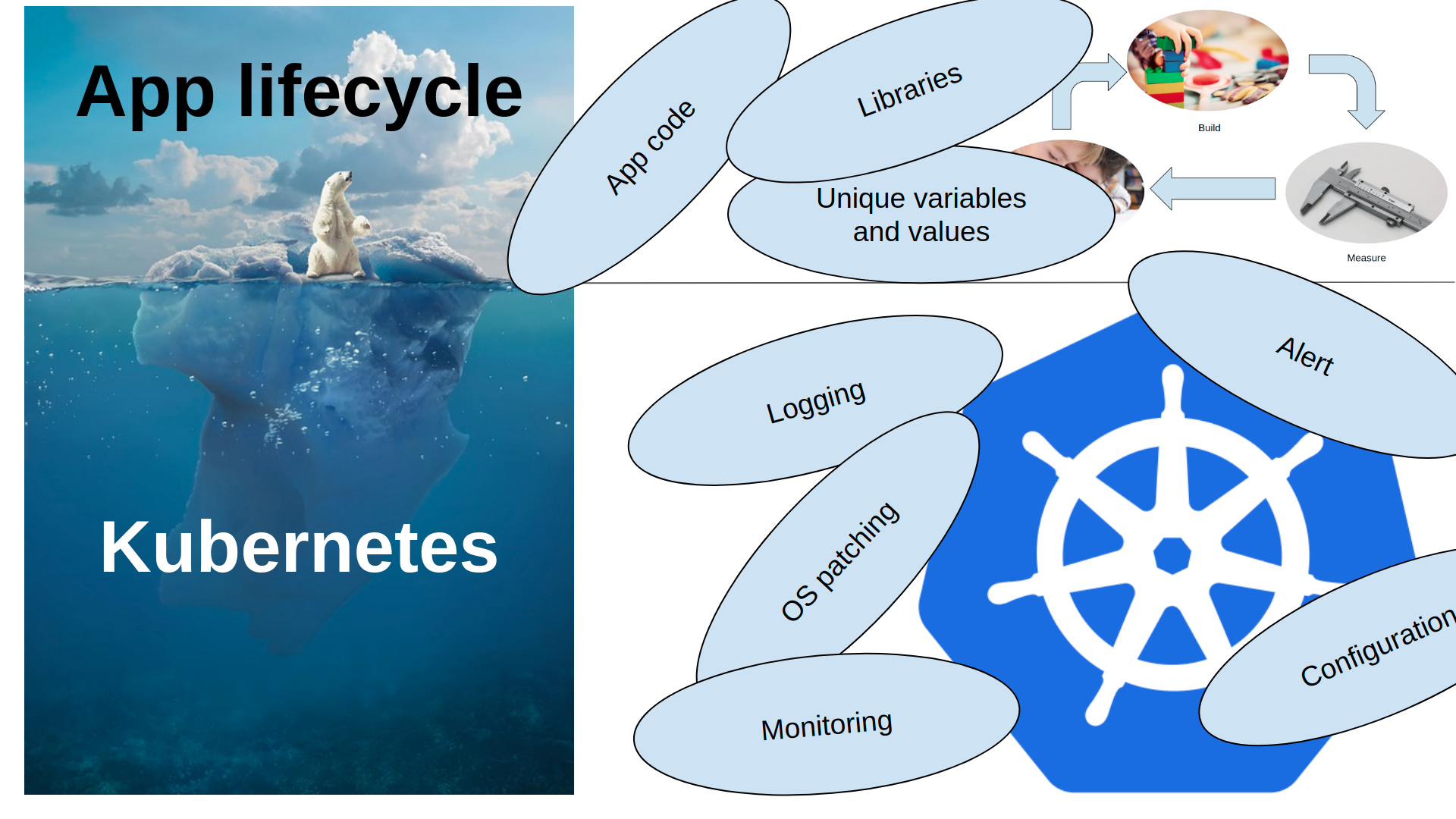
So what?
It reduces the two-week sprint of deployment to deploy, deploy, deploy. It reduces the wait time between the deployment.
But how?
- The docker image ship the OS along with the application.
- Kubernetes cover the running docker container in a box called a pod.
- The deployment controller manages the pods, Which makes them easy to upgrade and rollback.
If you would like to deep dive into deployment, there are two beginner sessions dedicated to the deployment. However, it is an admin guide.
What are the other benefits of using Kubernetes?
A containerized applications run anywhere.
What does it mean? Once the developer packed the application into a docker image, he pushes it to the Docker repository. Based on our docker repository permissions, the image can be pull from anywhere.
Anywhere, means what?
Kubernetes portability
It means a developer can run the Kubernetes on his/her laptop and push it to the docker image repository.
The tester can pull it from the docker repository. And run it on their laptop or the test lab.
Once the testing is over administrator can run over,
- Own premises datacenter.
- Bare metal servers configured with Kubernetes.
- Number of public and private clouds like
- Amazone Web service (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Microsoft azure.
- Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform
Yes, now the develop ->test->prod cycle automated with CI/CD pipeline, which is altogether a different part of it. We are not going to discuss it now. Let us continue with Kubernetes. Along with this, we will discuss one of the main advantages of using Kubernetes, portability.
How to create objects in Kubernetes?
Before going to portability, let us see the object creation in Kubernetes. There are two methods to create an object in Kubernetes.
Imperative object configuration
In simple words, it is a command-line operation. Everything like object names, arguments or flags should be specified in the command.
Declarative object configuration
Kubernetes objects can be created, updated, and deleted by mentioning all the configuration information in a YAML file. This method is called declarative object configuration. This method also allows us to keep multiple configuration files under a directory and create all the objects in a single command.
The command is as simple this.
**kubectl -f
Now let us go back to the portability.
What is portability in Kubernetes?
Let us put it all together.
Kubernetes has lots of objects like pods, deployment, cron job, and so on. And the data or information is stored under the volume, persistent volume, config map and secrets.

Docker images are the building blocks of Pods. It can be storge in the docker repository.
The docker images are lightweight it comes in Mbs. ( There are exceptions.)

All the objects can declare in the object definition file.
Ya, we reached there, now the things are easy. Make the Docker repository available to the new setup.
Copy paste the definition file to the new setup. There are other methods also we are not detailing here.
Note: - If you have any data in the persistent Volume. Then it should transfer to the new setup.
That’s it.
If it is a simple application, it starts to run in seconds. If it is a heavy application, it may take few minutes.
It is as simple as that. We brought the application from one data centre to another.
Now think of a traditional data centre.
Mark the cabling, take the network diagram. to prepare the plan Booking a lorry.
It takes months or years together to move the data centre from one to another.
